The future of grassroots and decentralized media lies in federated trust networks, not in the current, merely, replicating the centralized, broadcast-focused models of the #dotcons. There are problems with simply copying #dotcons as #FOSS that is replication without change, simply mimicking the #dotcons replicates their flaws, including centralized control and scalability issues that lead to degradation in quality and trust.
Broadcasting models focus on individual reach rather than collective, community-driven engagement. For example, #bluesky and #mastodon scale without accountability, over-scaling singular nodes results in reduced moderation quality, fostering misinformation and people’s dissatisfaction.
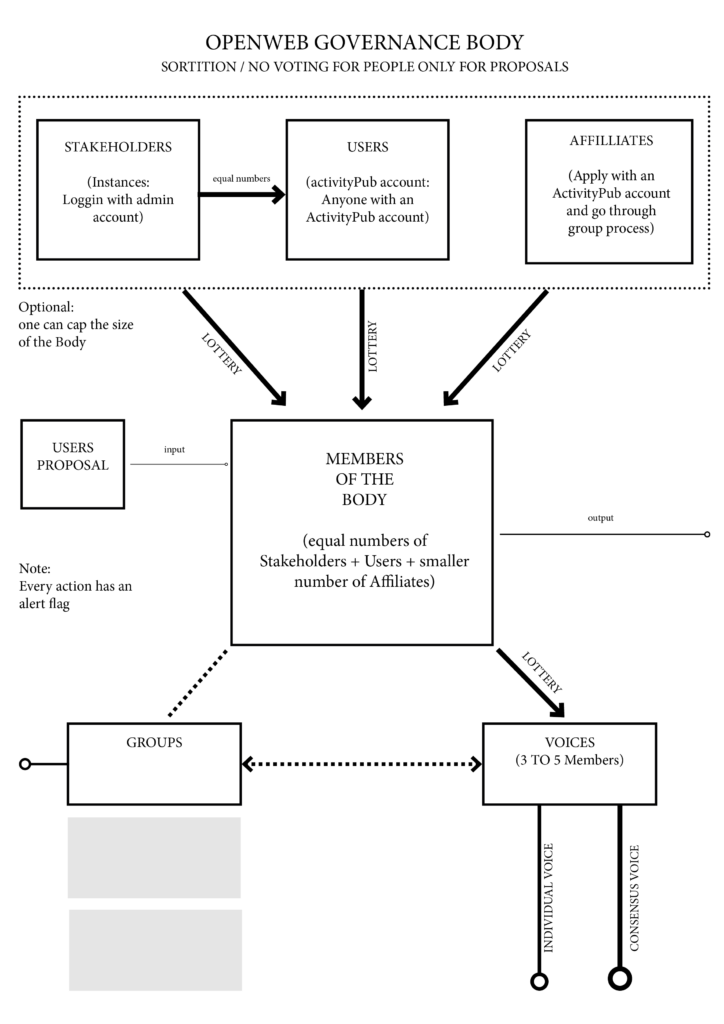
There is a strong case for human scale federated trust networks, with human moderation for quality. In the #OMN, every instance is moderated by a competent crew responsible for maintaining content standards. Expanding requires growing the moderation team to sustain quality. This path ensures people and communities gravitate toward smaller, well-moderated instances, balancing scale and trust.
- Tag flows for better categorization, we need to create distinct admin tools for personal and news flows, so networks can handle content more effectively and avoid mixing purposes.
- Decentralization with purpose, federated networks with #ActivityPub, allow instances to share content while maintaining autonomy. This prevents over-centralization and supports diverse community voices.
- The #4opens—open process, open data, open licences, and open standards, are baked into the #OMN to maintain transparency and community ownership.
An example of this is the #OMN is key to rebooting #Indymedia The #OMN project provides a framework to reboot alternative media, like #indymediaback, in a way that prioritizes the “native” quality, trust, and community moderation. The first steps toward a reboot will be integrating federated systems and trust-based governance to revitalize the platform. This is key, learning from the past, avoiding a rehash of dead indymedia, the #OMN emphasizes creating new structures based on lessons learned, particularly the importance of human-centred workflows. With the ultimate goal is to restore indymedia domains to active use while avoiding past pitfalls.
For those wanting an #indymedia reboot, supporting #OMN projects is crucial, as it is directly aligned with this vision. The #OMN and federated trust networks offer a roadmap for reclaiming decentralized media spaces. By focusing on trust, moderation, and the #4opens, we move beyond the failures of centralized #dotcons and create sustainable, community-driven alternatives. This isn’t just a revival of the old; it’s a necessary evolution to meet the challenges of today’s digital paths.