Back then, we were teetering on the edge of a digital cliff, with the open internet hanging in the balance. There were two insightful perspectives capturing the crossroads we are at: Phil Windley argued that the open internet was a historical fluke, while Dave Winer suggests that what we were seeing was merely the ebb before the next wave of the #openweb arrived.
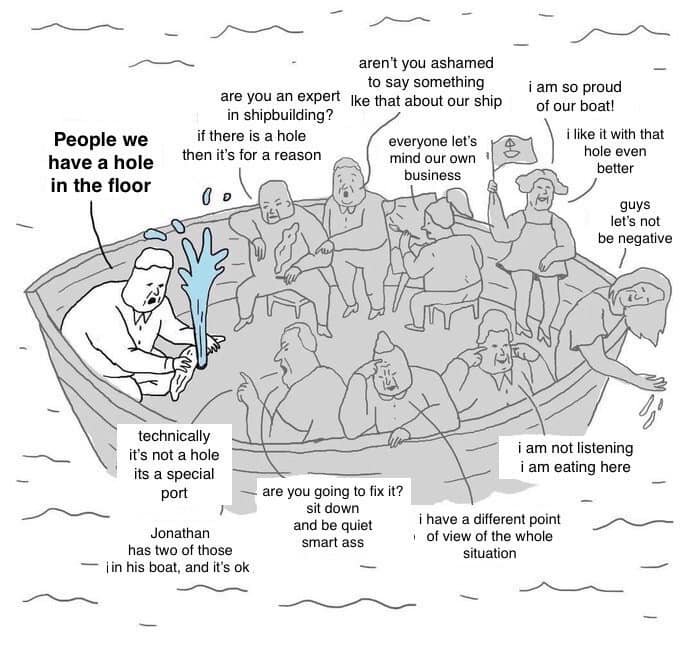
With this enclosure of the digital commons, #PhilWindley perspective, is a sobering one. Though he has updated his post, he used to see the internet early open nature as an anomaly—an accident of history. In this view, the open internet as we knew it is essentially finished. That once-thriving commons have been systematically enclosed by corporate silos—the #dotcons like Facebook, Google, and Amazon—that now dominate the digital landscape. What remains outside these silos is, according to this perspective, withering and dying. The vision of a decentralized, user-controlled internet has been overwhelmed by the centralized, profit-driven motives of these tech giants.
His argument is that decentralization is hard, perhaps too hard for most people to handle. This reality, combined with the fact that these silos provide convenience, user-friendliness, and perceived safety, has led people to choose them over the messy and challenging world of a truly #openweb. People have traded freedom for convenience, security for walled gardens, and the vibrant chaos of the commons for the curated safety of #dotcons. The digital commons have been enclosed, and it was a bleak view.
On the other side, Dave Winer offered a more hopeful perspective. He believes that the history of the internet and the web comes in waves—periods of openness followed by enclosure, which then recede to allow for another wave of openness. In his view, Phil Windley’s observation might not be wrong, but it’s not the end of the story. Rather, it’s the ebb of the tide before a new wave of the #openweb surges forward. The potential for decentralized, and open paths is always there, and it’s a mistake to assume that the current moment is the end of the line.
#DaveWiner argument rests on the idea that the desire for openness and freedom is cyclical. When centralized systems become oppressive, restrictive, or exploitative, there will be a counter-movement that pushes back. The nature of technology, innovation, and humanistic creativity ensures that “native” paths, and protocols will emerge to challenge the status quo.
There is a logic to the digitization of everything. The internet and #openweb built on top of it, is a living example of what happens when this logic is let loose: a tsunami that crashes over every part of our cultures, breaking old structures and opening up possibilities. The storm is not over. Just as the early web opened up commons that were later enclosed, the current wave of enclosure is broken by a new wave of #4open decentralization paths.
What Has Changed in the Last Decade? Looking back at what I wrote nearly ten years ago, the fundamental dynamics haven’t changed. The dotcons have only grown more powerful and more entrenched, but at the same time, the counter-forces have also begun to stir vigorously. Movements like the #Fediverse, based on #ActivityPub, #Nostor and to a lesser extent #Bluesky have grown into real usable decentralized social paths, together with this, we are dipping our toes back into peer-to-peer technologies, this wave is evidence that the storm of digitization is still alive.
Yes, the #dotcons did enclose the first wave of commons, when we stupidly took their digital algorithmic drugs. But the defences of the dotcons are very weak, the only thing holding most people is their addictions, nobody thinks they are healthy any more. The logic of digitization continues, and as long as there are waves, there is hope for the current openweb reboot.