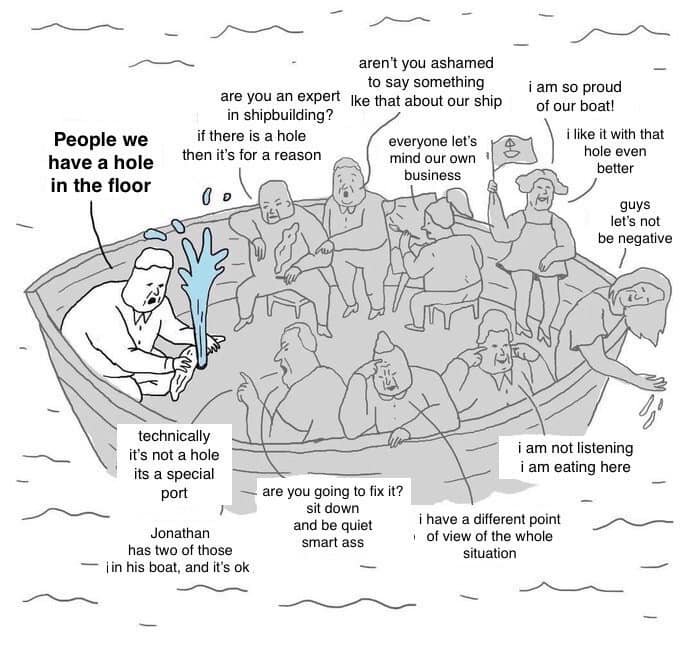
It can be hard explane this, as people make the needed change complex, it is not, yes, it’s messy and the are no simple answers. So a first step is composting the #techshit:
- Raw waste → The constant flood of mainstreaming, broken promises of #dotcons, bad-faith #NGO capture, shallow “innovation theatre.” This is the smelly mess we are swimming in.
- Shovel work → Activists and communities don’t just sit in the mess. We work to turn it over, exposing the rot, adding oxygen. This is critique, transparency, and the #4opens in action.
- Aeration → Sunlight + openness turns stink into something useful. Lies are exposed, corruption made visible, hidden power structures dragged out into the light.
- Soil of change → The same waste that poisoned us can become fertile ground for new growth, but only if we do the work of turning it. This is how trust-based networks sprout, how projects like the #OMN emerge.
What it means in practice:
- Don’t just delete the shit – we instead compost it. Bad actors, bad processes, and bad tech are made visible and contextualized.
- Don’t hoard the shit – silos just trap the stink. Share, federate, distribute – so communities can add their own oxygen.
- Don’t wallow in the shit – critique alone is not enough. The point is to grow fertile alternatives.
The composting metaphor says: yes, we’re drowning in #techshit, but we have the tools to turn it into the soil for something humane, resilient, and alive. #KISS

The #OMN is a simple project. But simplicity is deceptive, what makes it difficult for many #fashernista and #mainstreaming people is not the code, not the servers, not even the logistics. The difficulty is that the #OMN is rooted in a different path of human nature.
It isn’t designed to fit the old path of #stupidindividualism. It isn’t built to serve the greed of #dotcons. It isn’t here to bend the knee to the #deathcult. The #OMN is designed as a transition tool, a bridge to a different path, commons, trust, a living path. Once people arrive, they can build what they like. That’s why the #OMN isn’t just tech, it’s a toolkit for social change and challenge.
#KISS. Keep it simple. Keep it real. I’ve been building this bridge for 20 years, agenst strong counter flows, we were all pushed off the path when we handed our voices to the #dotcons. When #openweb culture gave way to #stupidindividualism, I was ready to give up.
So I bought a boat and sailed away. #boatingeurope. Not a metaphor – it’s survival. But then came the #ActivityPub reboot, the #openweb with the #Fediverse rose again. I came back. Because there was hope, there still is.
And now – five years into this reboot – we face the next predictable crisis: #mainstreaming, the sell-outs, the “respectable voices”, the NGO parasites. Yep, it’s normal, it happens to every alt project. And now it’s happening here.
The solution? Compost the mess. Not to attack individuals – most of them aren’t important. What matters are the paths they push us down. Because their “common sense” is the real danger. These are “common sense” paths that turn living networks into dusty, dry creeks.
That’s why I keep writing the #hashtag stories: to make these hidden paths visible. So we can choose differently by seeing what’s going on. . Then act to compost the #techshit to grow something real.
I started by saying the #OMN is a simple project, let’s illustrate this with the #OMN Process
- Gather
People, projects, and content come together.
Anyone can publish by trust, share, and tag media.
Use open standards (#4opens, #openweb).
No gatekeepers, just openness mediated by trust.
- Describe
Content is enriched with metadata -tags, descriptions.
Human-readable and machine-readable.
Stories are linked by meaning, not silos.
- Share
Feeds are syndicated (via RSS, ActivityPub, etc.).
Content flows across the network.
Local projects display, remix, and reframe.
- Distribute
Decentralized hosting: many small servers, not one #dotcons.
Mirroring + redundancy = resilience.
No central point of failure.
- Contextualize
Communities add their perspective, framing, and translation.
Different views can co-exist on the same story.
Keeps the commons diverse and contested, not controlled.
- Compost
Bad ideas, #mainstreaming, and #NGO co-option are made visible.
Instead of only deleting, we contextualize and critique.
This “compost” becomes fertile ground for better growth.
- Grow
New media projects emerge from the toolkit.
Each can shape the #OMN path to fit their community.
A living, adaptive commons.
Principles in practice, KISS → tools stay simple, human-readable, small pieces that fit together. #4opens → open data, open code, open process, open standards. Trust-based networks → rooted in commons, not control. Resilience → many weak ties are stronger than one big silo.
The #OMN is not an app you install. It’s a set of processes + tools to move us from isolation to commons, from #dotcons back to #openweb.