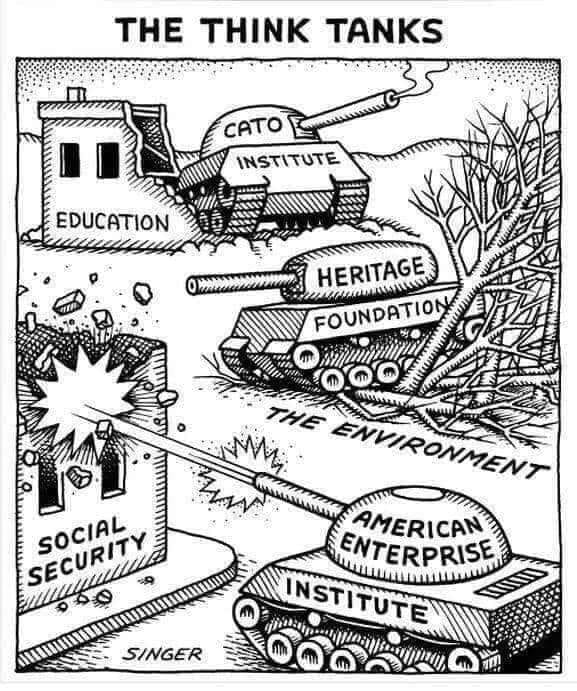
The current state of our political systems, particularly the electoral process, raises fundamental questions about the nature of democracy and representation. The problem is the system is designed to maintain the supremacy of the powerful, perpetuating conflicts and minimizing real democratic engagement.
Elections, rather than fostering democracy, exacerbate divisions and repeatedly fail to address critical issues. Parties capitalize on trivial matters, manipulate voters, and converge on worshipping of the #deathcult with policies that benefit commercial interests.
Historically, elections have been chosen as a means to exclude the majority from meaningful involvement in power, reflecting a distrust of democracy by the powerful. The UK’s political model, shaped in the 18th century, survived the introduction of universal suffrage largely intact, maintaining a system where elected representatives are disconnected from the interests and needs of the real people.
Despite alternatives such as participatory democracy, popular assemblies, and sortition (random selection like the #OGB), powerful, and everyday interests stifle their implementation. These alternative social technology models prioritize #4opens community involvement, deliberation, and consensus-building over the spectacle of elections.
Participatory democracy, when well-designed, has proven effective in addressing complex and divisive issues. Citizens’ assemblies and constitutional conventions have successfully tackled issues such as equal marriage, abortion, and climate policy, where elected representatives have struggled. This in a native, messy form is how all activism is organised.
The next step needs to build up grassroots democracy with a project like the #OGB to supplement, push aside and then replace traditional parliamentary chambers. Such a system would ensure that decisions are made by a representative sample of society, rather than by career politicians shaped by money and lobbying.
In conclusion, by embracing participatory democracy, we can create a system where everyone has a chance to shape the decisions that affect their lives. You can find more information on the #OGB project https://opencollective.com/open-media-network/projects/openwebgovernancebody and support this on the link.